Are you having trouble connecting to Facebook or Twitter? Has your internet connection slowed down to the point that it’s become unusable?
Don’t blame your internet service provider just yet. The reason for this could be a program consuming bandwidth in the background.
In this post, you’ll learn how to monitor the bandwidth usage of your applications and how to put an end to it.
Method 1: Task Manager
The easiest way to monitor your network activity would be through Task Manager. This application shows all the programs that are currently running in your PC. This feature is available on Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10.
Open Task Manager by hitting Ctrl + Shift + Esc. You can also right-click Start and select Task Manager.
For most users, the Task Manager will only display programs that are currently running. Click More Details to get more information.
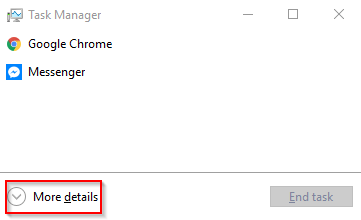
The expanded view will not only show a list of running applications, but it also tells which are consuming the most resources — including network activity.
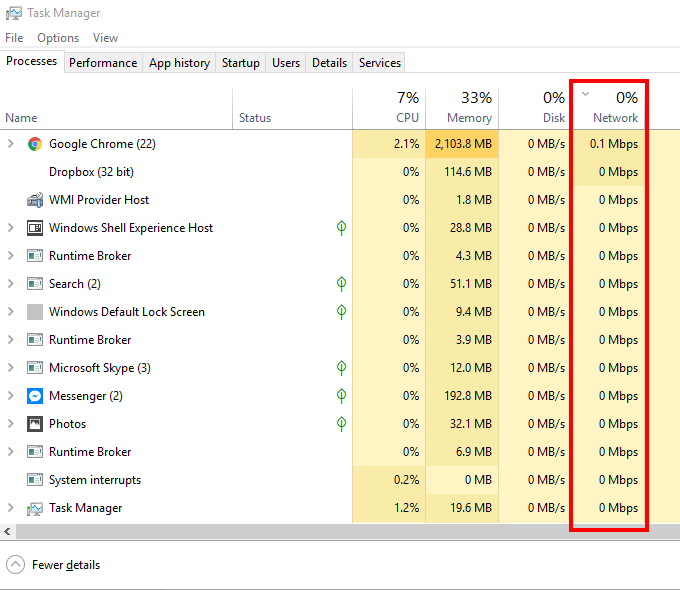
Clicking Network will arrange the column in ascending or descending order. Putting the list in descending order lets you see which programs are getting the most network usage.
To can force applications to stop. Right-click the program and select End Task.
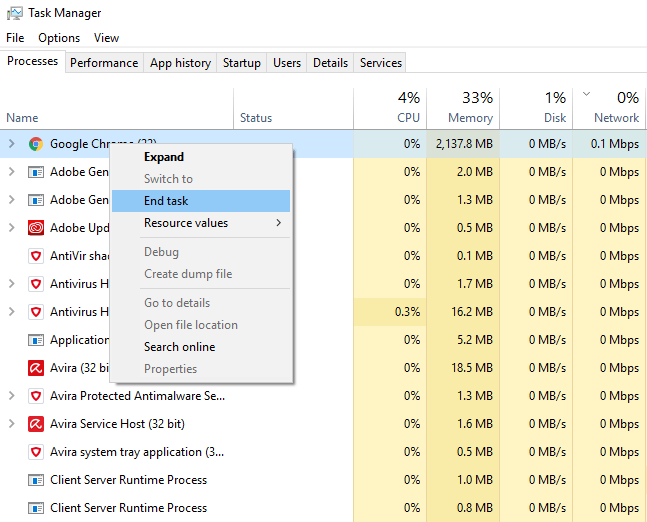
Note: Some running applications are crucial for Windows to continue working. Ending these types of tasks will cause your computer to shut down.
Method 2: Resource Monitor
You can use Resource Monitor instead to find which apps are connecting to the internet. Resource Monitor is the better tool to use if you want to dive deeper into the details.
Open Run and type RESMON. Windows 8 users might have to type RESMON.EXE instead.
This will open Resource Monitor. Click the Network tab. This will show you all the network activity on your computer.
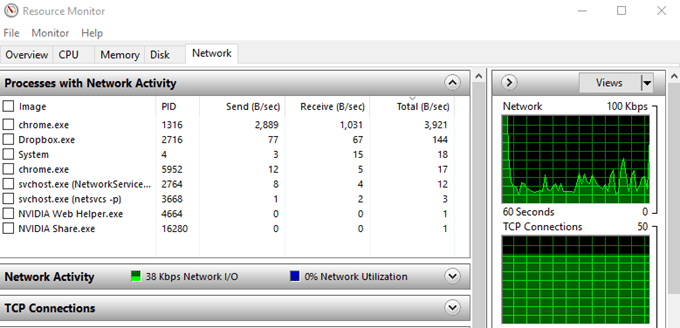
The Processes With Network Activity window is composed of five columns.
- Image – The name of the application
- PID – Shows you the process ID number
- Send (B/sec) – This is the average number of bytes per second the app sent in the last minute.
- Receive (B/Sec) – This is the average number of bytes per second the app received in the last minute.
- Total (B/Sec) – Total bytes per second the app used in the last minute.
If you’re seeing unfamiliar programs in the list, right-click on it and select Search Online.
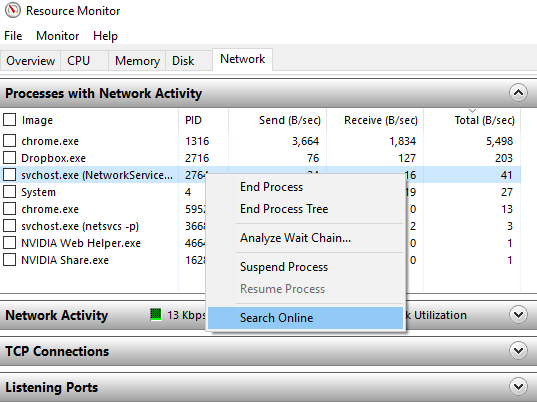
Clicking Search Online will prompt Windows to do a web search of the application in question.
Should you find an application that’s using way too much bandwidth, right-click it and select End Process.
Method 3: Third-Party Tools
You can find a number of third-party programs online to help monitor your bandwidth usage. This is great for students or anyone who has a cap on internet usage.
While these apps give you more control over your bandwidth allocation, they can be pricey. Most of them aren’t free while others operate on a freemium model.
But still, if monitoring network usage is important to you then it could be worth spending money on a solution. For most people, however, the first two methods should
Related Posts
- How to Fix App Notifications in Windows?
- Preparing for Windows 10 End of Support: Upgrading to Windows 11
- How to Fix a “This file does not have an app associated with it” Error on Windows
- How to Fix an Update Error 0x800705b4 on Windows
- How to Resolve “A JavaScript error occured in the main process” Error on Windows
Christopher Jan Benitez is a freelance writer for hire who provides actionable and useful web content to small businesses and startups. In his spare time, he religiously watches professional wrestling and finds solace in listening to ’80s speed metal. Read Christopher’s Full Bio
