You may think that you need to restart your computer in order for registry changes to take place. Not necessarily. Restarting the explorer.exe process performs the same function. Explorer.exe is the program component in Windows that provides the Windows Shell. The Windows Shell or Explorer creates and presents the entire Windows user interface, such as the Taskbar, the desktop, Windows Explorer, the notification area (system tray), Start menu, dialog boxes, and interface controls.
You may have heard about terminating the explorer.exe process using the Task Manager. Using the Task Manager may be effective, but it is forcibly killing the process instead of terminating it properly, giving the process the change to exit safely and completely. In Windows 10, you use the task manager to end the process. There is a hidden option in the Start menu in Windows 7 and Vista and an extra function in the Shutdown menu of Windows XP that allows you to terminate and restart the explorer.exe process correctly.
Windows 10
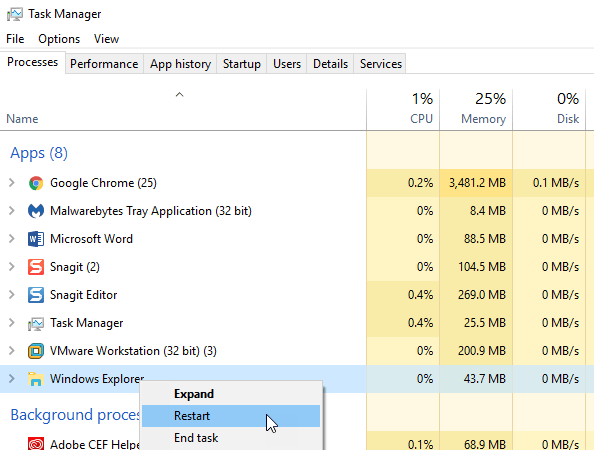
In Windows 10, you first have to open the Task Manager by pressing CTRL + SHIFT + ESC on your keyboard or by typing in task manager after clicking on Start.
Up at the top where it says Apps, find Windows Explorer and right-click on it. One of the options will be Restart. In Windows 10, the process is killed and then automatically restarted. You don’t have to go to File – Run New Task to start it up again like you do in Windows 7 and earlier.
Windows 7 and Vista
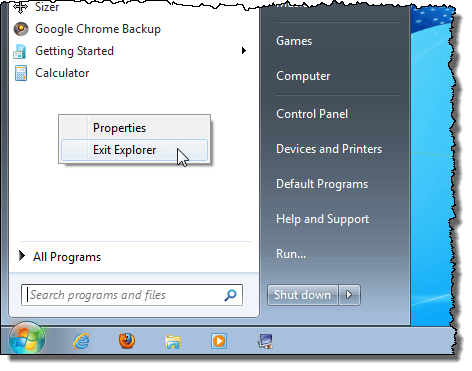
To correctly shutdown the explorer.exe process in Windows 7 and Windows Vista, open the Start menu. Hold down the Ctrl and Shift keys and right-click on any empty space on the Start menu. A short, popup menu displays with two options. Select the Exit Explorer option.
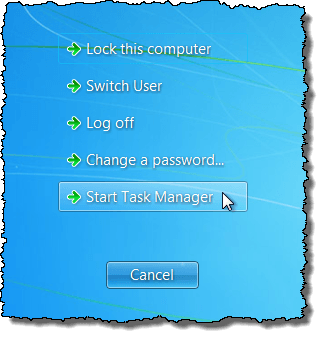
The Taskbar goes away and the desktop icons seem to disappear. To access the Task Manager to restart the explorer.exe process, press Ctrl + Alt + Delete. A screen displays with five options. Select Start Task Manager.
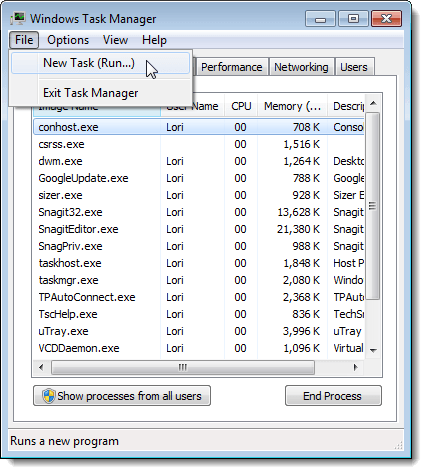
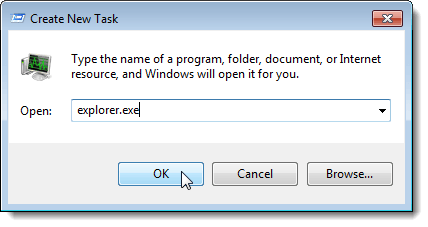
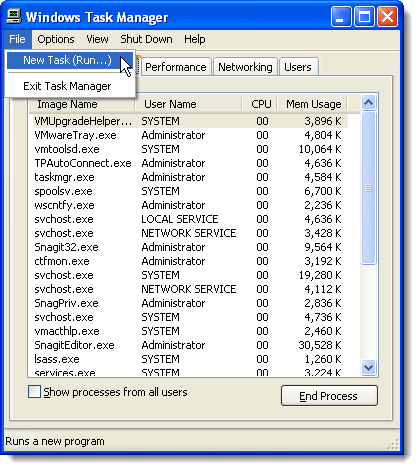
In the Task Manager, select New Task (Run…) from the File menu.
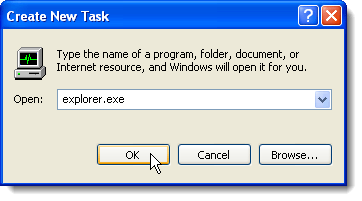
The Create New Task dialog box displays. Type “explorer.exe” (without the quotes) in the Open edit box and click OK. The Taskbar, desktop, and other components of Windows are restored.
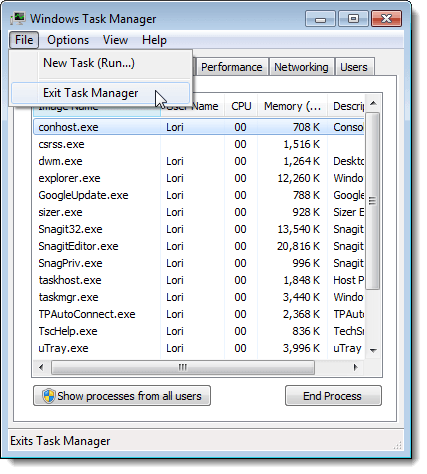
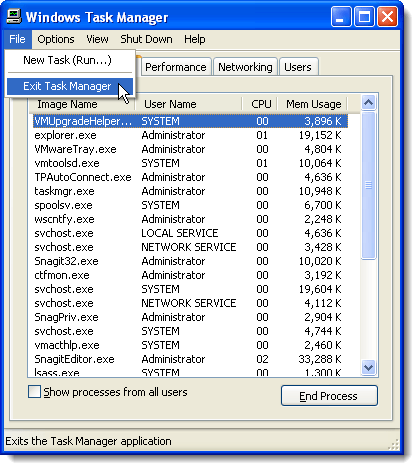
To close the Task Manager, select Exit Task Manager from the File menu.
Windows XP
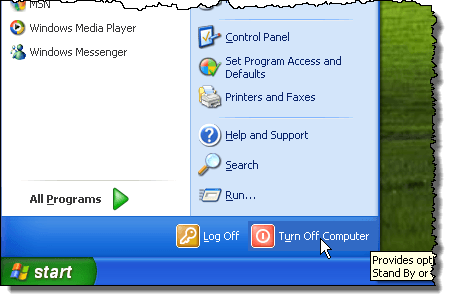
To correctly shutdown the explorer.exe process in Windows 7 and Windows Vista, open the Start menu and click the Turn Off Computer button at the bottom of the menu.
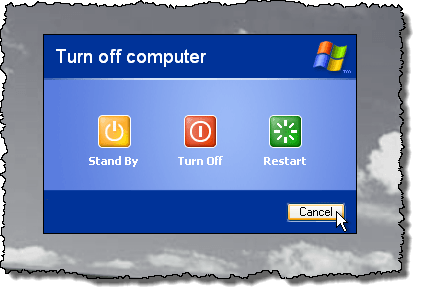
The desktop turns shades of gray in the background and the Turn off computer dialog box displays with three options and a Cancel button. Press and hold Ctrl + Alt + Shift and click the Cancel button.
Just like in Windows 7, the Taskbar goes away and the desktop icons seem to disappear. To access the Task Manager to restart the explorer.exe process, press Ctrl + Alt + Delete. In the Task Manager, select New Task (Run…) from the File menu.
The Create New Task dialog box displays. Type “explorer.exe” (without the quotes) in the Open edit box and click OK. The Taskbar, desktop, and other components of Windows are restored.
To close the Task Manager, select Exit Task Manager from the File menu.
Exiting the Explorer process cleanly allows you to shutdown Explorer without risking locking up your Windows session if you forcibly kill the explorer.exe process using the Task Manager or the taskkill command. Enjoy!
Related Posts
- How to Reset Your Computer Password If You Lock Yourself Out
- Best Ways to Quickly Hide Windows Applications
- How to Boot into Safe Mode in All Versions of Windows
- Transfer Files from Windows XP, Vista, 7 or 8 to Windows 10 using Windows Easy Transfer
- How to Change the Clock To Military Time in Windows