Windows has a built-in troubleshooting tool that lets you diagnose connectivity problems on your computer. When this tool detects a problem with your network, it fixes them automatically. Sometimes, it points out the problem and recommends probable solutions. At other times, the network troubleshooter describes the problem without proffering any solution.
A good example of the third instance is the “Windows could not automatically detect this network’s proxy settings” error. Obviously, this message tells you that there’s a problem with your network’s proxy settings. What it doesn’t reveal is how to fix the problem.
That’s because issues relating to proxy configurations are multifaceted and often complex to fix, particularly if you don’t know where to look or what to do.
Rebooting your router and computer may fix the problem. If the issue continues, one of the 9 troubleshooting solutions listed below should do the magic.
1. Restart Your PC’s Network Adapter
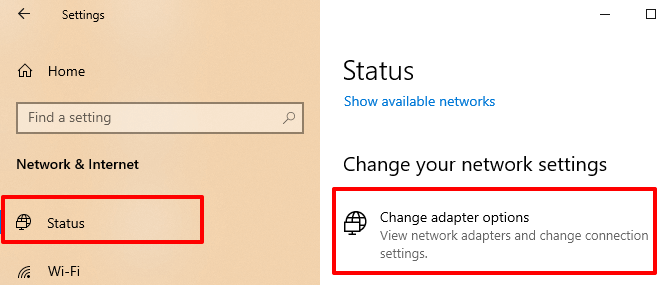
Power-cycling your network adapter is a quick way to fix simple and complex connectivity problems on your computer. Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status and click Change adapter settings.
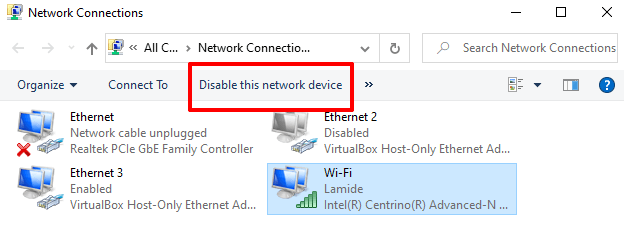
Select Wi-Fi (if you’re using a wireless connection) or Ethernet (for a wired/LAN connection) and click Disable this network device on the toolbar.
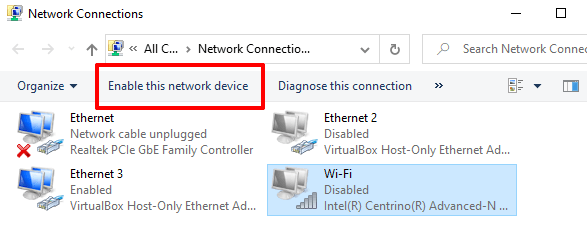
Wait for about 10-30 seconds and re-enable the network adapter. Select the network and click Enable this network device.
2. Check Adapter IP Settings
If the error persists and you still cannot access the internet, disable any manual IP address or DNS configuration assigned to your network adapters. Allowing Windows to automatically obtain IP and DNS server addresses for your connections can eliminate this error.
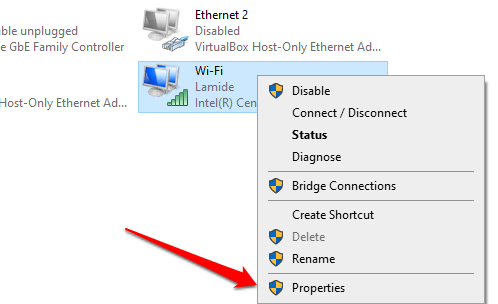
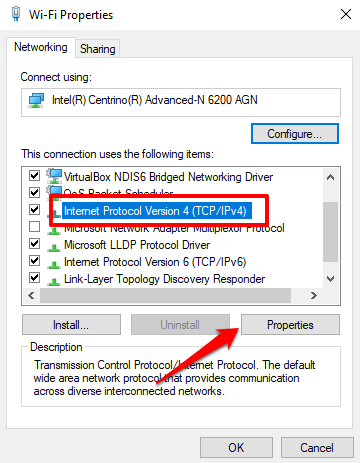
In the Network Connections windows (Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Change adapter settings), right-click on the network (Wi-Fi or Ethernet), and select Properties.
Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
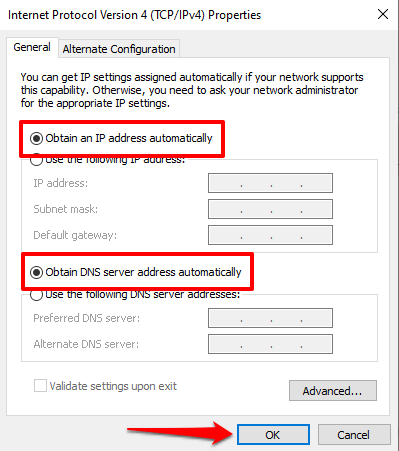
In the General tab, select Obtain and IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically. Select OK to save.
3. Disable Proxies, Firewalls, and VPN
Routing your internet through firewalls, VPNs, and proxies can cause network interference that result in error messages like “Windows could not automatically detect this network’s proxy settings.” Disable your VPN, firewall, and other network apps and check if that restores internet access.
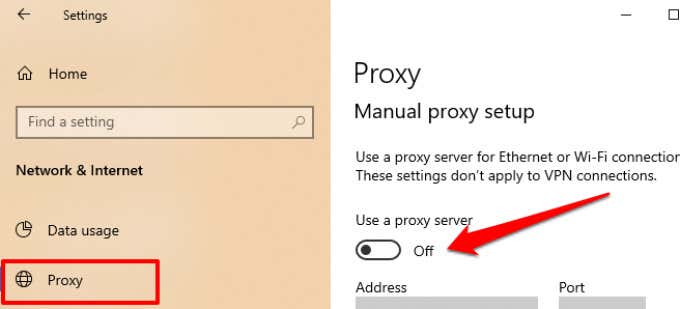
Additionally, go to Settings > Network & Internet > Proxy and toggle off Use a proxy server to disable any manual proxy setup on your computer.
4. Update Your Network Driver
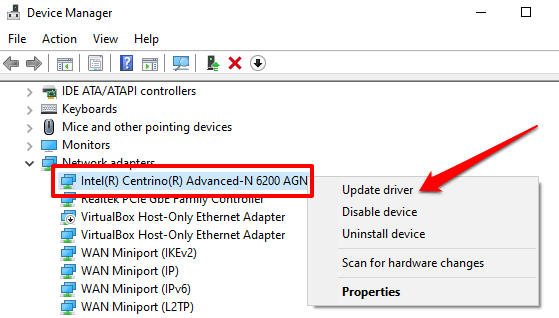
Drivers get corrupt, outdated, and buggy every now and then. These often birth connectivity problems and render the internet unusable on your computer. Head to the Device Manager and check if there’s an update available for the network driver.
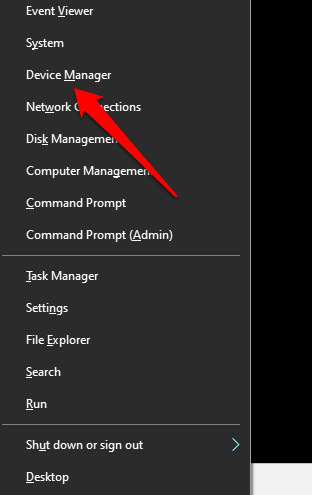
1. Right-click the Start menu icon and select Device Manager on the Quick Access menu.
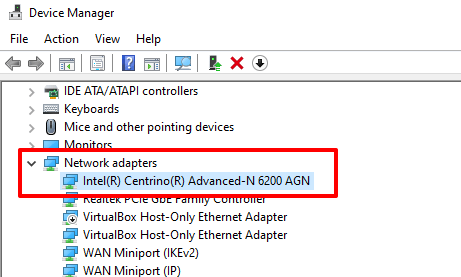
2. Expand the Network adapters section, right-click on your network driver, and select Update driver.
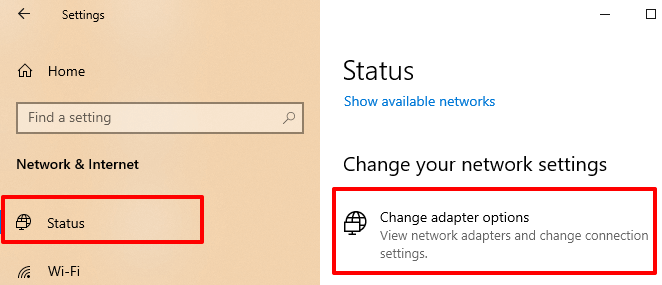
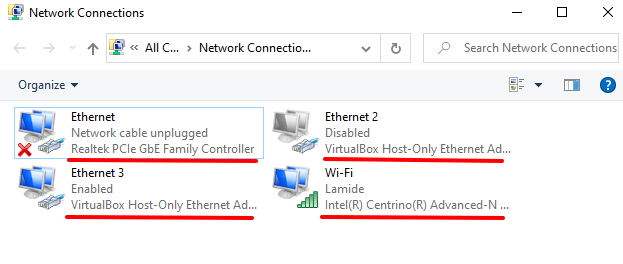
Quick Tip: If there are multiple drivers in the Network adapters section and you have no idea which one’s the Wi-Fi or Ethernet adapter, go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Change adapter options.
You’ll find the name of your PC’s Ethernet and Wi-Fi drivers labeled below the network types. Now you know which driver to update in the Device Manager.
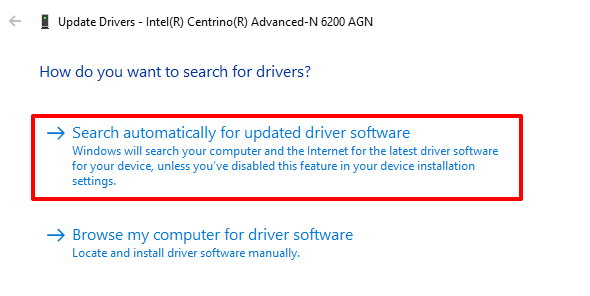
3. Next, select Search automatically for updated driver software.
Windows will search your computer and the internet for a new version of the network adapter. If it finds any, follow the prompt on the page to download and install the update.
5. Roll Back Network Adapter
Windows Updates sometimes ship with driver updates. While these driver updates bring new features, they may contain bugs that’ll break certain features on your computer. Some driver updates may also be incompatible with your computer.
If the “Windows could not automatically detect this network’s proxy settings” error commenced after a recent Windows or driver update, roll the driver back to the previous version and restart your computer.
1. Launch the Device Manager, expand the Network adapters section, and double-click your network adapter.
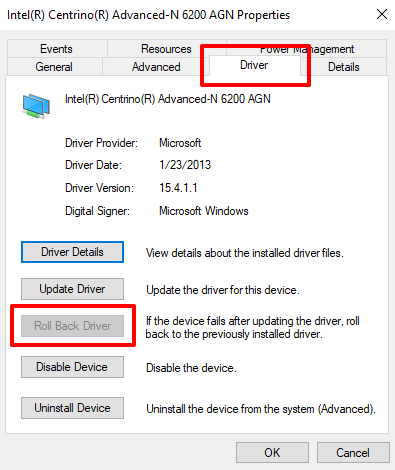
2. Go to the Driver tab and click the Roll Back Driver button.
Follow the instructions on the next page to roll back the driver and restart your computer afterward.
Note: If the Roll Back Driver button is grayed out, that means you (or Windows) didn’t install any driver update.
6. Check for Malware Infection
Malicious programs and files can corrupt and damage important network files and settings. Scan your PC for malware using Windows Defender or reputable third-party anti-malware programs. These will help detect and remove stubborn malware infections responsible for network failures.
7. Reset Your Computer’s Internet Configurations
This entails resetting the Windows Socket (Winsock) and the TCP/IP stack. These network settings determine how network applications communicate with each other on your computer. You may experience connectivity errors like the “Windows could not automatically detect this network’s proxy settings” if these network functions become corrupt.
Follow the steps below to fix Winsock errors and corrupt TCP/IP settings using the Command Prompt tool.
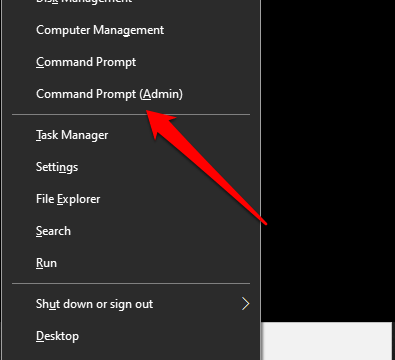
1. Right-click the start button and select Command Prompt (Admin).
2. Run the commands below individually (i.e. one at a time). Press Enter after each command and wait for a success message before you run the next command.
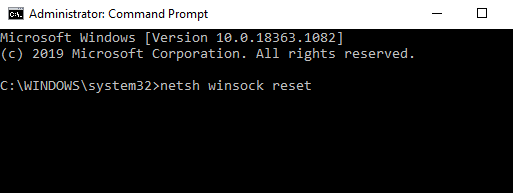
netsh winsock reset
netsh int ip reset
ipconfig /release
ipconfig /renew
ipconfig /flushdns
3. Restart your computer.
These commands will clear your PC’s DNS cache, revert changes made to your computer’s Winsock settings, and rewrite registry keys used by the TCP/IP.
Note: You may need to reconfigure some network-related programs like your VPN, firewall software, etc. after resetting the Winsock and TCP/IP catalog.
8. Reset Your PC’s Network Settings
If the problem persists and you still can’t access the network, perform a network reset. That will reset VPN and proxy servers, reinstall network adapters, and revert all network configurations back to their original state.
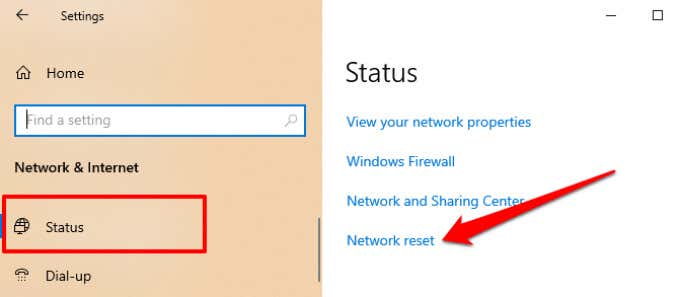
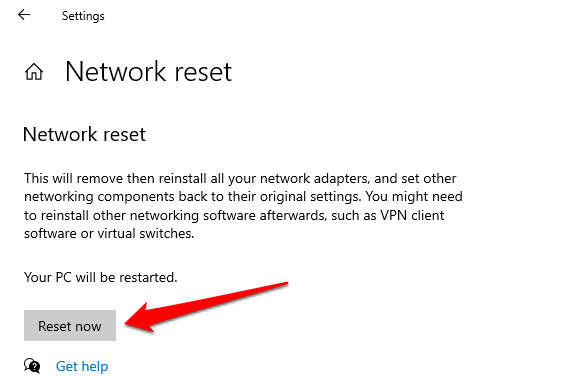
Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Status and click Network reset at the bottom of the page.
Click the Reset now button and click Yes on the confirmation prompt.
Windows will sign you out and restart your device, so make sure you close all applications before you reset network settings—so you don’t lose any unsaved tasks/documents.
9. Restore Your Computer
You should consider restoring your computer to a previous state when network connectivity was working perfectly. The Windows System Restore feature will remove recently-installed programs and drivers that may be responsible for the problem. Your personal data (files, documents, pictures, videos, etc.) will remain intact, so you have nothing to worry about.
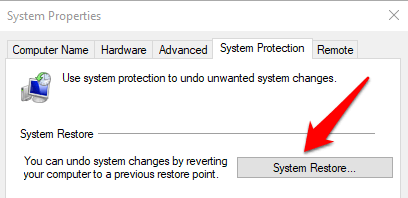
Go to Control Panel > System > System Protection and click System Restore.
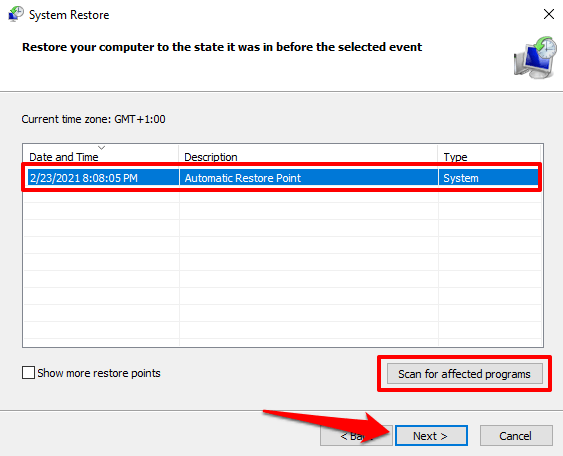
Select a restore point on the list and click Next to proceed.
Pro Tip: Click the Scan for affected programs button to see a list of apps that’ll be deleted during the system restore process.
Can’t find any restore point in this menu? The System Restore feature is probably disabled on your computer. Learn how to enable or disable system restore in Windows.
Restore Internet Connectivity
If none of these recommendations resolve the problem, try using the Windows System File Checker (SFC) tool to repair corrupt system files messing with your PC’s network configurations. As a last resort, perform a clean reinstall of Windows 10.
Related Posts
- How to Fix App Notifications in Windows?
- Preparing for Windows 10 End of Support: Upgrading to Windows 11
- How to Fix a “This file does not have an app associated with it” Error on Windows
- How to Fix an Update Error 0x800705b4 on Windows
- How to Resolve “A JavaScript error occured in the main process” Error on Windows
Sodiq has written thousands of tutorials, guides, and explainers over the past 4 years to help people solve problems with Android, iOS, Mac, and Windows devices. He also enjoys reviewing consumer tech products (smartphones, smart home devices, accessories, etc.) and binge-watching comedy series in his spare time. Read Sodiq’s Full Bio