Those of you who have been using Windows for some time may have already bore witness to the “RPC Server is Unavailable” error. This is one of the more common errors you can run into while using the Windows OS and often causes confusion to more inexperienced Windows users as to why it popped up in the first place.
You needn’t worry, however, as it isn’t a serious or dangerous error, so all of your programs and data are safe. What RPC stands for is Remote Procedure Call, which is a method that some applications will use to communicate with other applications that are running on the same computer.
What this means is that RPC allows different processes to communicate with one another in order to perform a task.
It operates similarly to networking in that the RPS server will open a port, gage a response from the destination service or server, send a packet once a response is received, and then transfer the task data to the destination service or server. After the job is done, the whole process operates in reverse to send data back to the initiating program.
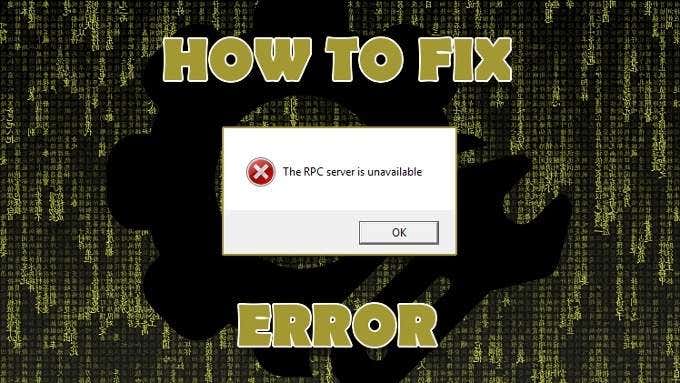
An RPC Server Error Has Occurred
RPC server errors aren’t exclusive to the Windows OS nor just a single computer. The RPC method is used on most current operating systems. The cause for an RPC error will usually occur on one computer, but the cause may actually be found on an entire network. Luckily, in this article, we’ll be looking into both possibilities.
So what exactly causes an “RPC Server is Unavailable” error? When one service on your computer needs to communicate with another, it will contact the RPC server on your computer to initiate the exchange.
The RPC server will open up a few ports in order to listen for a message and issue one back. If the RPC server fails to receive a response, is unable to write to memory, cannot open a port, or is simply unavailable, then the error is triggered.
Fixing RPC Server Errors
There are three ways to go about fixing one of these errors on a computer running Windows 10. The most common of the three would be that the RPC service is not even running. The other two, issues with the network or corrupted registry entries, are less likely but may still occur.
When you receive one of these errors, or any Windows error really, the first thing to try is a full reboot. A reboot will fix a temporary issue related to the RPC server. If a reboot doesn’t resolve the error, you’ll want to dive into one of the fixes below.
RPC Service Not Running
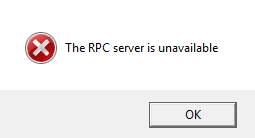
After a reboot, check to see if the RPC Service is causing the problem.
- Open the Task Manager by right-clicking on the Task Bar and selecting it from the list.
- Navigate to the Services tab and then Open Services.
- Scroll to the Remote Procedure Call service. It should be running and set to Automatic. If it’s not, change it.
- Navigate to the DCOM Server Process Launcher. This too should be running and set to Automatic. Again, if results are different, make the necessary changes.
Network Problems
Issues with TCP or your firewall can stop RPC from working. This is true even if the call is made internally on your own computer as the RPC Server still uses the network stack for communication purposes.
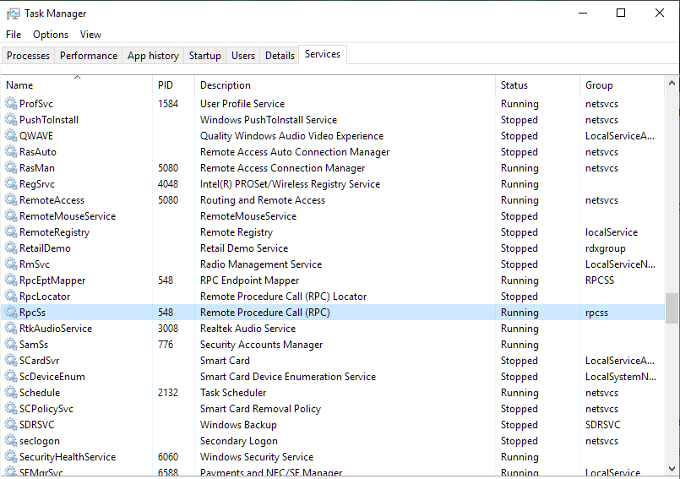
- Pull up the Control Panel and select Network and Internet (view by set to Categories) or Network and Sharing Center (set to either large or small icons).
- Click the Ethernet link located next to Connections: and then Properties in the popup window.
- The IPv6 and File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks should both have a checkmark. If they do not, add it and click OK and retry the task that caused the error. If they are already marked, then you’ll need to check your firewall.
- Select the Windows Firewall in Control Panel.
- For third-party firewalls, you’ll have to experiment with the settings. You should give it a once over but don’t change anything if it’s a firewall you’ve been using for a while.
- Locate Remote Assistance and make sure it is enabled for Domain, Private and Public networks. Then save any changes you have made.
Registry Corruption and Complications
If everything has been fine up to this point, then the last thing you can take a look at is the registry entries that control the RCP and DCOM services for corruption. I don’t recommend tinkering with the registry, especially for beginners, so to be safe, we’re going to back up the registry before messing with anything.
- Enter regedit into the search box on the Task Bar. Click on Registry Editor when it appears.
- Click Computer from the left side window and open the File tab. Select Export from the menu.
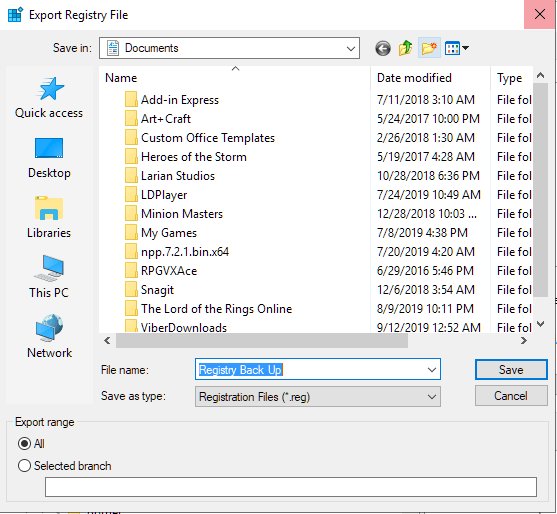
- Choose a name and location for the saved file and hit the Save button.
Once a back up of all registry files has been created, you can check the entries for the RPC and DCOM services.
Navigate to the following key:
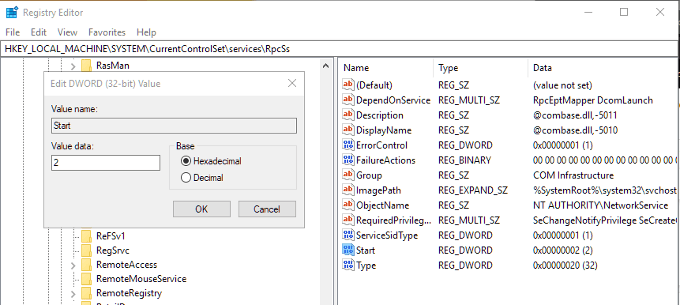
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\RpcSs
In the right pane, right-click Start and then Modify… Set the value to (2).
Next, you’ll need to navigate to both the keys below:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\DcomLaunch
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\RpcEptMapper.
Do the same thing with Start as was done in the previous step.
Related Posts
- How to Fix App Notifications in Windows?
- Preparing for Windows 10 End of Support: Upgrading to Windows 11
- How to Fix a “This file does not have an app associated with it” Error on Windows
- How to Fix an Update Error 0x800705b4 on Windows
- How to Resolve “A JavaScript error occured in the main process” Error on Windows
Former US Army IT communications specialist who began his online blogging career in 2016. Joseph has over 10 years experience in the IT industry as both an analyst and communications expert. He’s a night owl and an avid Red Bull consumer who spends most of his downtime enthralled by online gaming and website building. Read Joseph’s Full Bio
