The ability to upgrade Ubuntu to the latest version had many benefits, including using the latest software and getting access to new security patches.
Before upgrading to Ubuntu, keep the following points in mind:
- Once you upgrade, the only way to revert to a previous version is to reinstall it. This means you might lose your existing data.
- Before doing anything, backup your files and folders.
- Make sure you have a stable Internet connection.
- It will take at least an hour depending upon your Internet speed.

Why Would You Want to Downgrade Ubuntu to a Previous Version?
There are times when a new release of Ubuntu has some errors or bugs in the software code. When someone runs into these errors, either with a fresh installation or when installing a dual boot alongside Windows, they might want to downgrade to a previous version until the kinks are worked out.
You can downgrade Ubuntu by re-installing the previous release of the operating system. Unfortunately, unless Ubuntu is installed in a directory separate from your personal data and apps, they won’t be saved.
This is another reason it is imperative to back up all your data on an external hard drive.
There are several ways to upgrade to the latest Ubuntu installation. In this article, we will discuss the following methods:
- Graphical method.
- Software Updater Tool doesn’t find an update.
- Using Terminal and Command line.
- Use a Single Command line with zzupdate.
Upgrade to the Latest Version of Ubuntu
Ubuntu’s latest release is 19.10 and will be supported until July 2020. You can view the official release notes here. New Ubuntu users can download Ubuntu 19.10 desktop and server editions and install it.
For those who are already running Ubuntu, when a new version is released, upgrades are immediately available. A popup will often ask you if you want to upgrade to the newest release of Ubuntu.
If you are currently running 18.10, it’s easy to upgrade to 19.04. If you are using an older version (before 18.10), you will need to first upgrade to each subsequent version and then upgrade to 19.04.
Upgrade From Ubuntu 18.10
Don’t forget to make a backup of your folders, files, and settings before proceeding in case something goes wrong.
- To update, open the Software & Updates app.
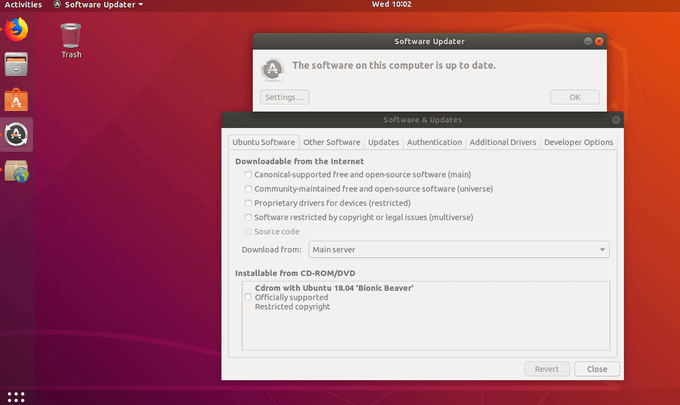
- Run a check for updates, and you should see that a new version of Ubuntu is available for download (if you are checking after the release date).
- You can also upgrade using the command line below:
sudo do-release-upgrade -c
The Graphical Method
Another way to upgrade Ubuntu is by using the built-in graphical tools from the standard Ubuntu desktop. You can also use terminal commands.
Standard releases of Ubuntu offer users an upgrade to new standard releases by default. Long-term support (LTS) releases only offer upgrades to new LTS releases.
An example is for those users running 18.04 LTS. When Ubuntu 18.10 was introduced, they weren’t offered the upgrade. Instead, when Ubuntu 20.04 LTS is released, then the offer will be provided. This behavior can be changed.
- On the top left-hand corner of the screen, click the Ubuntu logo button in GNOME Shell or the Activities button in Unity.
- Search for Update and click the Software & Updates shortcut.
- Or you can access the Software Updater application and open the window by clicking Settings.
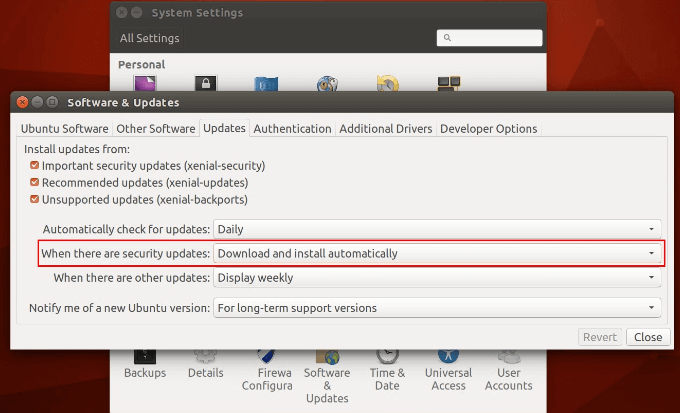
- Click Updates
- From the dropdown menu next to Notify me of a new Ubuntu version, choose between for long-term support versions or for any new version based on the type of update you want.
- When done, click Close
How To Upgrade If The Software Updater Tool Doesn’t Find an Update
If you don’t see an update, you can manually search for one.
- Start by pressing Alt+F2, type the following command, and press Enter.
update-manager -c
- This tool will check Ubuntu’s servers and let users know if a new version is available. Click the Upgrade button to get the newer version of Ubuntu.
- If you don’t see the upgrade message using the Software Updater tool, press Alt+F2. Enter the command below and click Enter.
/usr/lib/ubuntu-release-upgrader/check-new-release-gtk
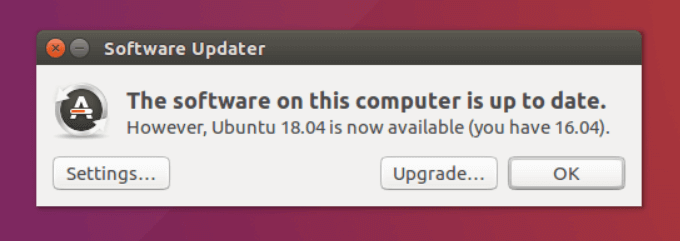
- If there is a new Ubuntu version available, click OK.
Upgrade Ubuntu Using Terminal & Command Line
Have you been using Ubuntu and want to update it to get the latest bug fixes, security patches, and application upgrades? It is relatively straightforward using the command line. The procedure outlined below works for Ubuntu versions 16.04, 18.04, and any other version.
It will also work for Ubuntu-based Linux distributions such as Linux Lite, Linux Mint, and elementary OS.
- From the desktop, open the terminal. You will find it by using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Alt+T or on the menu. You will have access to a terminal if you are logged in to an Ubuntu server.
- Enter the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
- Your system will next ask for your password. Use your account password. Then hit Enter.
- This command will update the local database of available Ubuntu packages and let your system know there are new versions. As seen in the screenshot below, after running this command, your system will display several URLs. These represent the available updates.
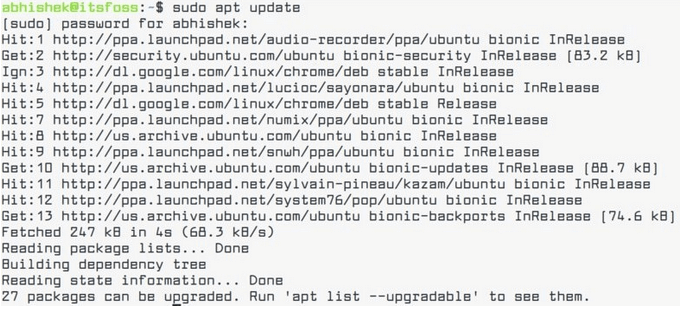
- To see specifically which packages have an upgrade available, run the following command:
apt list –upgradable
- Type yes or y to select the packages you want to upgrade.
- The sudo apt update checks your system for available new package versions. The sudo apt upgrade installs the versions you select.
Use a Single Command-Line With zzupdate
zzupdate is a command-line utility that will fully update server editions and Ubuntu desktop.
- Start by opening Software and Updates from an application launcher of the Gnome dashboard.
- Run a single-line command using the code below to upgrade Ubuntu:
$ curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TurboLabIt/zzupdate/master/setup.sh | sudo sh
This step skips the distribution upgrade by upgrading any older version to the latest available stable release. The source code for zzupdate is available in GitHub and is completely free to use.
When your Ubuntu upgrade is completed, zzupdate will automatically reboot your system.
Don’t forget to fully back up your current Ubuntu installation before you attempt any of the above methods to upgrade it.
Using the latest tested version of Ubuntu enables users to benefit from the application upgrades, fixed bugs, and security updates without having to resort to re-configuring or reinstalling their system.
Related Posts
David has a background in small business and lives in Australia. He is a WordPress and Ubuntu Developer who enjoys design, CSS and tech tool integration. Read David’s Full Bio
