Did you come across WDAGUtilityAccount when looking through the list of user accounts? Don’t worry—this specific user account is not a virus, and your system isn’t compromised. It’s part of most versions of Windows 11/10 Pro, Enterprise, and Education.
But what does it do? What is WDAGUtilityAccount? Read on to learn what this user account is and whether you can remove it.
What Is WDAGUtilityAccount
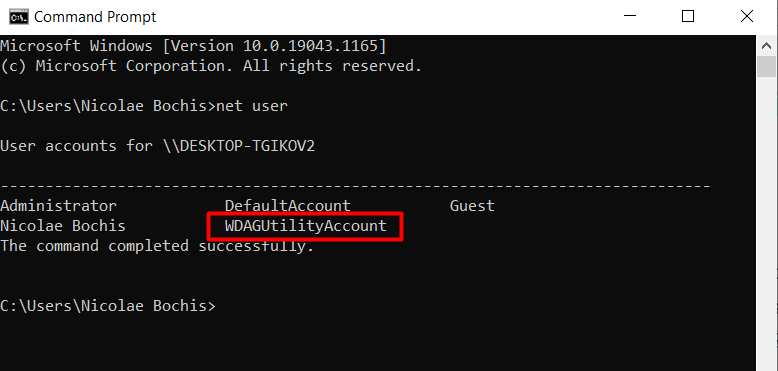
WDAGUtilityAccount is a built-in user account. It’s part of Windows Defender Application Guard (WDAG), which has been part of Windows 10 since version 1709. Usually, Application Guard is disabled by default. You can find it by opening the Command Prompt and typing the net user command.
Alternatively, if your computer runs on a Pro version of Windows, you can access this user account using the Computer Management tool.
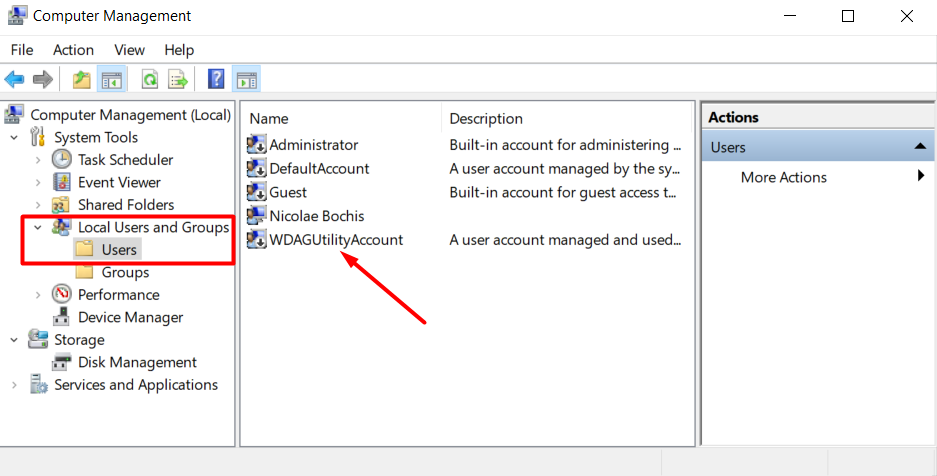
1. Type “computer management” in the Windows search box and click on the first result, which is the Computer Management app.
2. In the right panel of the app, go to System Tools > Local Users and Groups and click on the Users folder. That’s where you’re going to find the WDAGUtilityAccount user account.
As mentioned, this user account is used by the Windows Defender Application Guard tool. This tool is part of Microsoft Edge and Office 365, and it’s used to enable private browsing sessions. In other words, you can open a browser session that is completely isolated from your desktop. If you encounter any malicious software during that session, it won’t reach the rest of your system.
The tool opens the website you’re accessing in a virtualized sandbox, and WDAGUtilityAccount acts as the user account for that virtualization-based container. The user account is essential for the overall security of your Windows 11/10 system.
Is It Safe to Remove WDAGUtilityAccount or Change Its Settings?
Since this is a system-managed user account, you can’t actually delete it. Even if you could, you wouldn’t want to. It’s an important security element that protects you from specific security threats. You might occasionally see the account ask for administrator permission when you delete some types of files, but the account doesn’t have any negative impact on your computer.
That said, you can access specific settings and change them if needed.
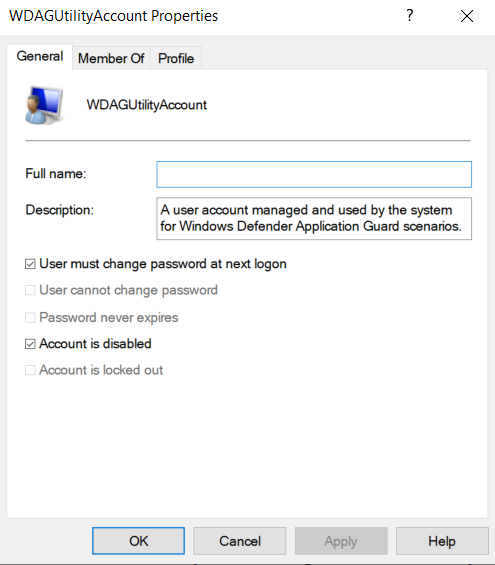
Go back to the Computer Management tool and double-click on the WDAGUtilityAccount user account. A window with various settings will open.
You should leave the default settings as they are unless you have an explicit reason to change them. If the account is disabled, like in the image above, you should un-check the Account is disabled option.
You can also rename the user account, but we don’t recommend doing so. It will break the Windows Defender Application Guard tool or prevent certain security features from working correctly.
In essence, WDAGUtilityAccount is a harmless system-managed user account that should be left alone. It doesn’t affect your computer in any negative way.
Enable Application Guard
As mentioned earlier, Application Guard is usually disabled by default. Here’s how you can enable it on Windows 11/10 Pro. You can also apply these steps on Windows 11/10 Enterprise and other versions that support WDAG.
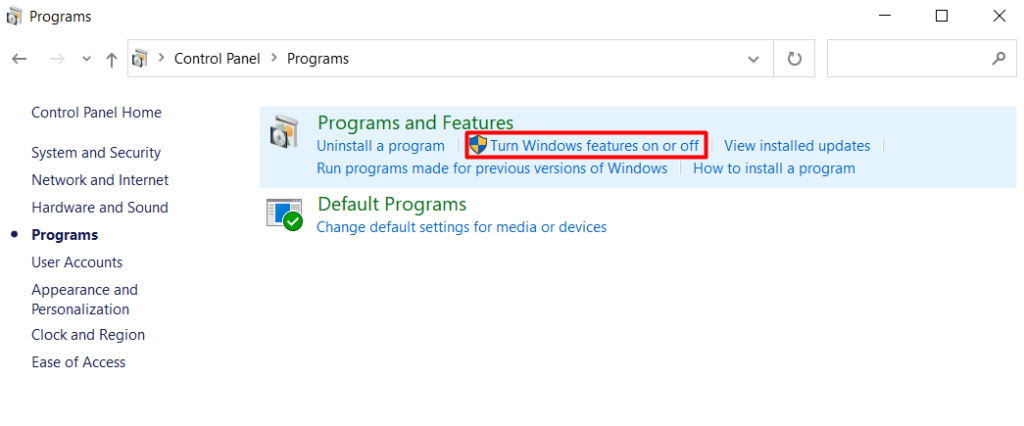
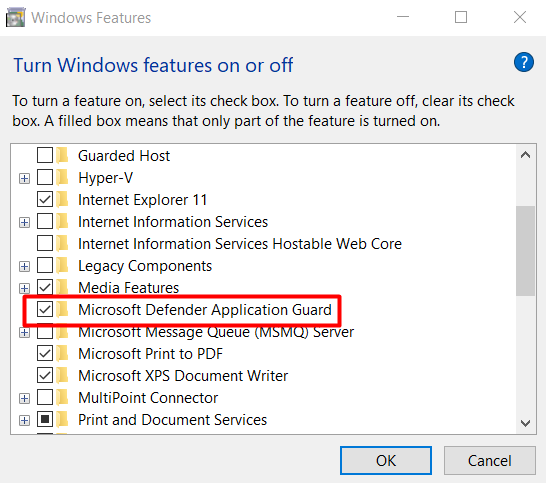
1. Go to Control Panel > Programs > Programs and Features and click on Turn Windows features on or off.
2. Scroll through the list of features until you find Microsoft Defender Application Guard and check the box next to it.
3. Click on the OK button and restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
If you can’t find this feature or it’s grayed out, your computer doesn’t support Application Guard or you aren’t running one of the supported versions of Windows 11/10, such as Windows 11/10 Pro or Enterprise. Upgrade to a higher edition of Windows if you’re using the Windows Home edition.
Related Posts
Nicolae is a Jack of all trades technology writer with a focus on hardware, programming languages, and AI image-processing software. Over the last five years, he has ghostwritten numerous tech how-to guides and books on a variety of topics ranging from Linux to C# programming and game development. Nicolae loves everything that has to do with technology and his goal is to share his knowledge and experience with others. Read Nicolae’s Full Bio