In other words, pseudo sudo commands
If you’ve ever used Linux or know someone who uses Linux, then you’ve probably heard of the sudo command. The command is a critical component to just about every Linux distribution and what it does is let you run a command as a different user, most notably the root user. On certain Linux distributions, you can log in as the root user by using the su command, but this is considered highly risky and no one ever does it.
Actually, it’s so dangerous that it’s disabled by default on Linux distributions like Ubuntu. Instead, you have to use the sudo command if you want to run a command as the root user. So what about Windows? Well, unfortunately, most people are logged into Windows as Administrators, which is the same as root user in Linux. However, Microsoft has tried to lessen the dangerous effects of being logged in as an Administrator by enabling User Account Control or UAC.
That way, even if the user has Administrative privileges, applications running under that account will not inherit those privileges unless it’s manually authorized by the user. This helps prevent malware and spyware from infecting a Windows user who is logged in as an Administrator.
So while Linux users have the sudo command, what do Windows user have? Are there alternatives that Windows users can use to run commands with elevated privileges? Is there a sudo command for Windows? In this article, I’ll talk about five alternatives to the sudo command for Windows users.
Note: Some of these tools are quite old now, so they may or may not work with the latest versions of Windows.
Windows Runas Command
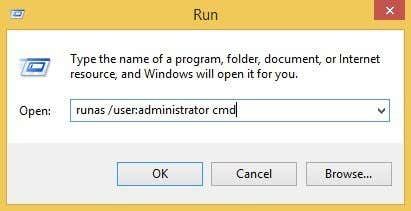
Windows has the runas command, which is the direct counterpart to sudo on Linux. Using the runas command, you can execute a script, program or command as a different user or as an administrator. The full syntax for the runas command is:
runas [{/profile|/noprofile}] [/env] [/netonly] [/smartcard] [/showtrustlevels] [/trustlevel] /user:UserAccountName program
If you wanted to open an administrative command prompt, you could type the following:
runas /noprofile /user:Administrator cmd
/noprofile will not load the current user profile. You can remove that if you need access to the user environment variables. If you wanted to open a text file using Notepad with administrator privileges, you could use this command:
runas /user:Administrator "notepad my_file.txt"
You can checkout the Technet page on runas for more information on how to use it.
Note that when using runas command, if you install a program or make changes to settings, etc., the changes will be made to the user account that you are running the command on. For example, let’s say you have user X who is a normal user and user Y, who is an administrator. If you log into X and then do a runas using the Administrator credentials, changes will be made to the Administrator’s settings, not user X.
So if you install an application by right-clicking on the EXE file and choosing Run as Administrator, it’ll get installed to the built-in Administrator user profile, not the one you are logged into. If you want true elevated privileges like sudo without the profile issues, check out the next alternative below.
Sudo for Windows – Sourceforge
Sudo for Windows is a free program you can install that will give you the same experience of the sudo command on Linux for Windows. The only difference is that Sudo for Windows “preserves the user’s profile and ownership of created objects” as stated by the developer. This is really handy if you like to use elevated permissions for installing apps or making changes to user locations like My Documents, etc.
It’ll give you Administrative privileges, but will keep all the changes in the current profile instead of the account you’re using to run the command with. The program requires .NET version 2.0, which you can’t download individually. In order to get 2.0, you have to install .NET Framework 3.5, which include 2.0.
Once you install Sudo for Windows, you need to add the user accounts that you to allow to have elevated privileges to a specific group created by the program called Sudoers. Right-click on My Computer or This PC and click on Manage. Then expand Users and Groups and click on Groups. You should see one called Sudoers.
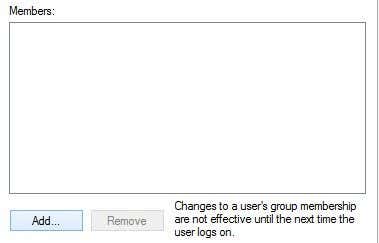
Double-click on Sudoers and click on the Add button.
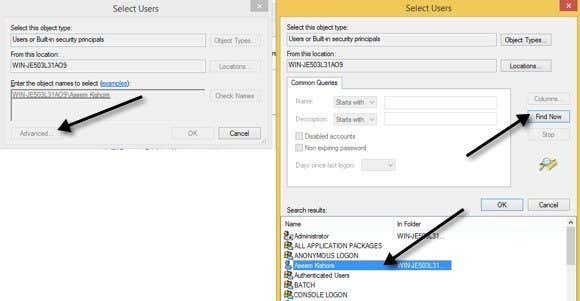
On the next dialog, click the Advanced button and then click Find Now. This will list out all users and groups on the system. Double-click the user you want to add.
Repeat this step for however many users you want to add. Then click OK and you should see the members listed in the Members listbox shown above. Click OK and now you should be able to use the sudo GUI and command. If you right-click on a program, you’ll see the Sudo option.
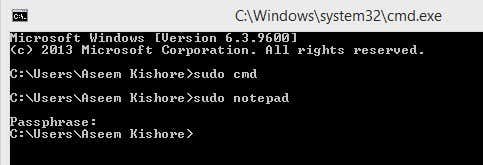
You can also open a command prompt and type sudo to run command with elevated permissions.
Overall, it’s pretty nifty and works very well. However, note that this particular program is really useful for launching programs or processes either via right-click or via the command prompt, but it’s not meant for running command line apps. For example, if you wanted to do sudo mkdir “c:\Program Files\new”, this won’t work using Sudo for Windows. For that functionality, there is another program called the same thing, but by a different developer. Read below.
Sudo for Windows – Luke Sampson
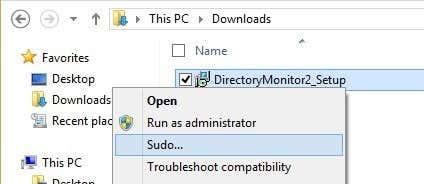
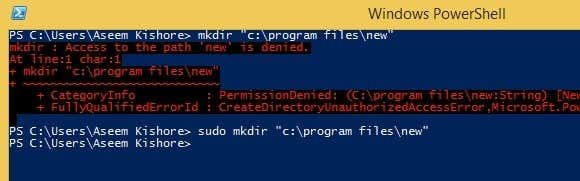
There’s another developer who wrote another Sudo for Windows that lets you execute command line apps too. So let’s go back to the example about creating a new folder in C:\Program Files. You can’t really do this by default.
Above I’m using PowerShell, but you’ll get the same error using the command prompt also. However, once you install Sudo for Windows, just add the word sudo to the front of the command and it works perfectly with no errors!
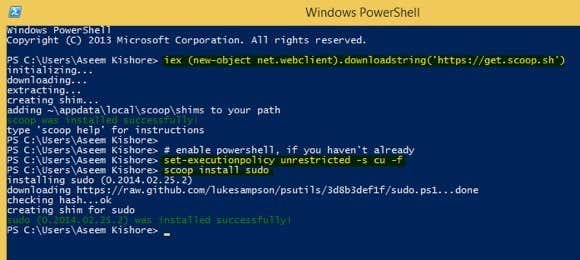
To install it, you need to open PowerShell and then type in the following commands in order:
iex (new-object net.webclient).downloadstring('https://get.scoop.sh')
set-executionpolicy unrestricted -s cu -f
scoop install sudo
If everything works OK, you should see the following output in PowerShell after each command:
That’s it! Now you can start typing in commands and adding sudo in front. The only annoying thing about this program is that the UAC window still pops up and you have click Yes for it to work. Even with that slight annoyance, the benefits are well worth it.
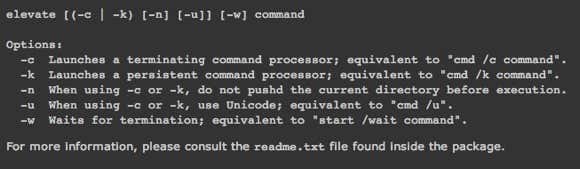
Elevate
Elevate is a program that works with UAC and doesn’t work exactly like sudo. With Elevate, it will change the executing user to Administrator like the runas command does. However, it’s useful for working in the command line or with batch files.
The main purpose of elevate is not to get around UAC, but to start a process in an elevated state from a non-elevated shell and then continuing on as normal even after the command has completed. Elevate is useful for scripting because you don’t have to worry about trying to script the whole right-clicking and running a command prompt as Administrator process.
Elevation PowerToys for Windows
For those of you who do a lot of work on the command line or work with scripts and batch files, then the Elevation PowerToys for Windows page has quite a few useful tools and scripts.
The script elevation power toys were created to overcome the frustrating aspects of UAC when trying to elevate a program from the command line or running scripts as administrators.
Hopefully, that’s enough tools and programs for you to make you feel like you’re actually using sudo on Windows. There’s no perfect replacement for it, but there are quite a few options that come close. If you use something else to elevate programs, commands or scripts in Windows, let us know in the comments. Enjoy!