If your computer is acting up, Windows Safe Mode can help you troubleshoot problems that interrupt or prevent Windows from starting normally. This way, you can make repairs on your own without having to visit a computer repair shop.
Safe Mode starts Windows in a basic state using a limited set of files and drivers so you can observe Windows and narrow down the source of the problem.
Prior to Windows 10, you could easily enter Safe Mode by repeatedly pressing the F8 key during a restart. Some computer manufacturers have since disabled the F8 key function, but you can still use the F8 method to enter Safe Mode in Windows 7, Vista and XP.
Here’s how to boot into Safe Mode in all versions of Windows.
Windows 10
In Windows 10, you can access Safe Mode using different methods including:
- The sign-in screen.
- From a blank or black screen.
- Using Windows Settings.
- From a recovery drive.
- Using System Configuration.
- Using the Shutdown command in Command Prompt.
Boot into Safe Mode from the Sign-in Screen
If you’re on the Windows sign-in screen, you can get into Windows safe mode in a few steps.
- Press and hold Shift while selecting Power > Restart.
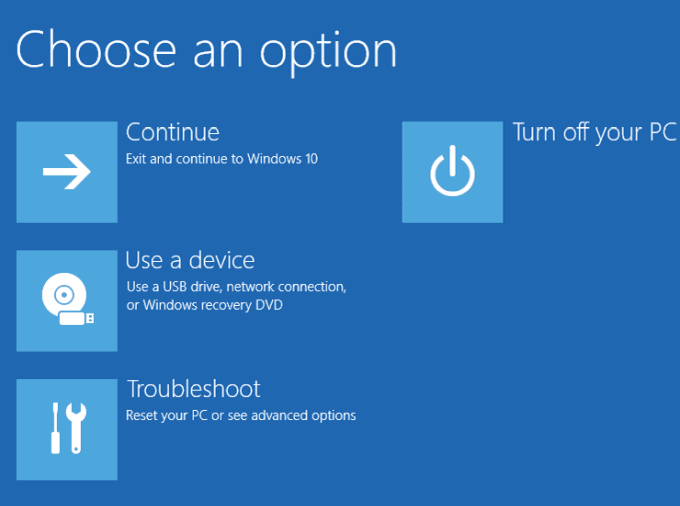
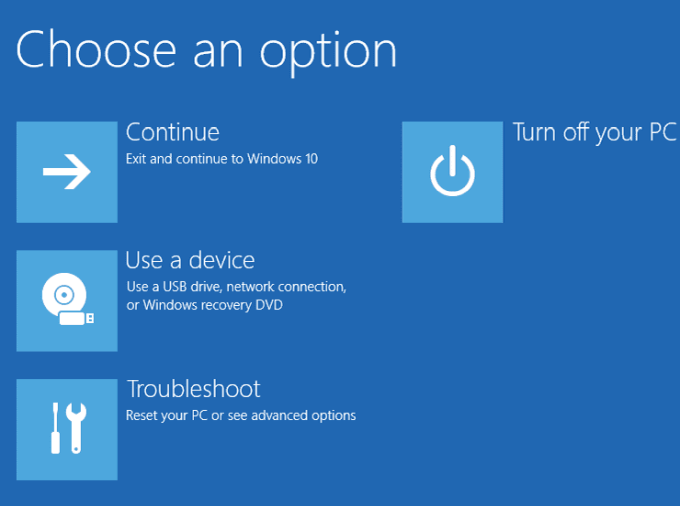
- Once your PC restarts, select the Choose an option screen.
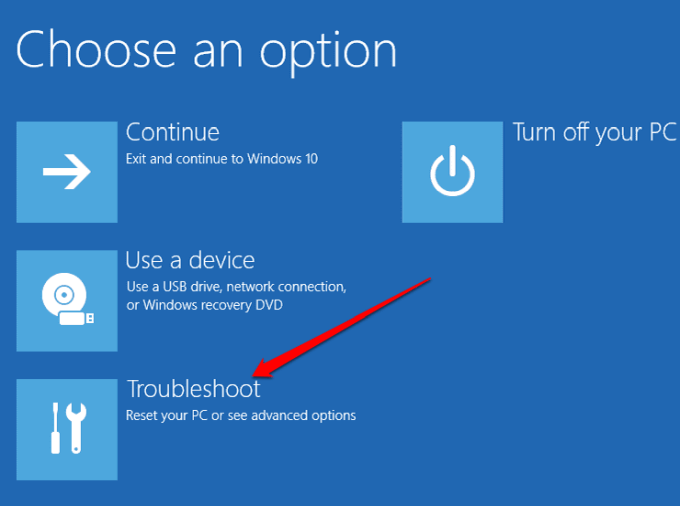
- Select Troubleshoot.
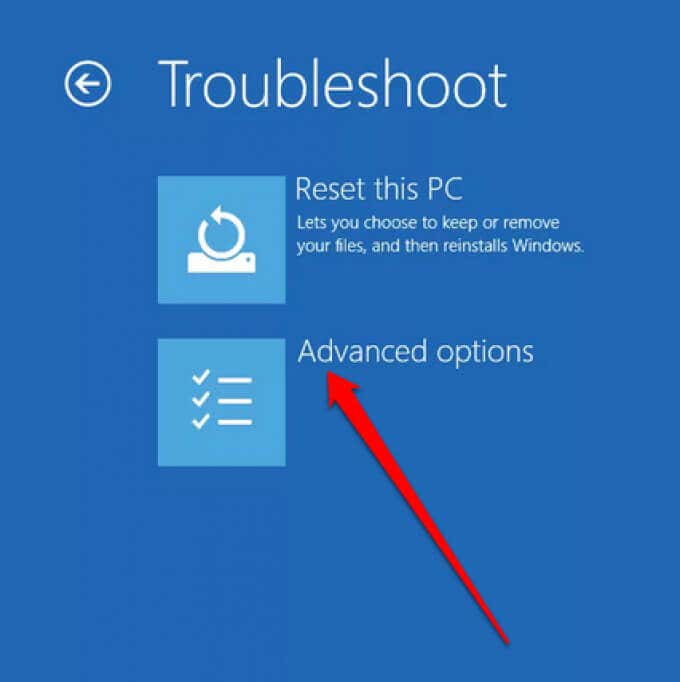
- Next, select Advanced options.
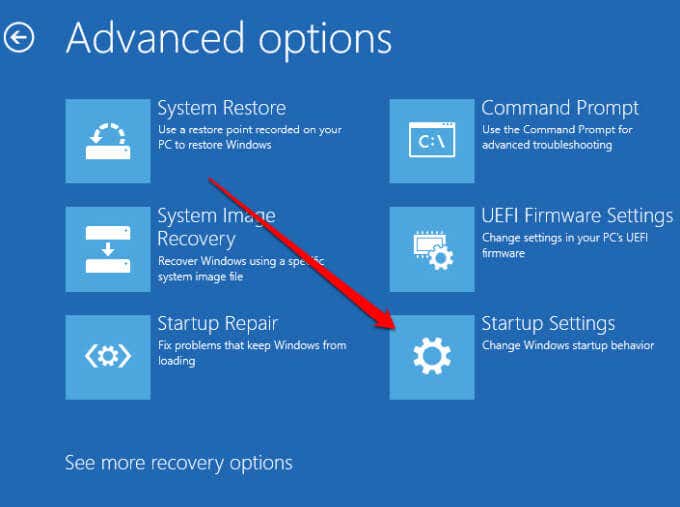
- Next, select Startup Settings.
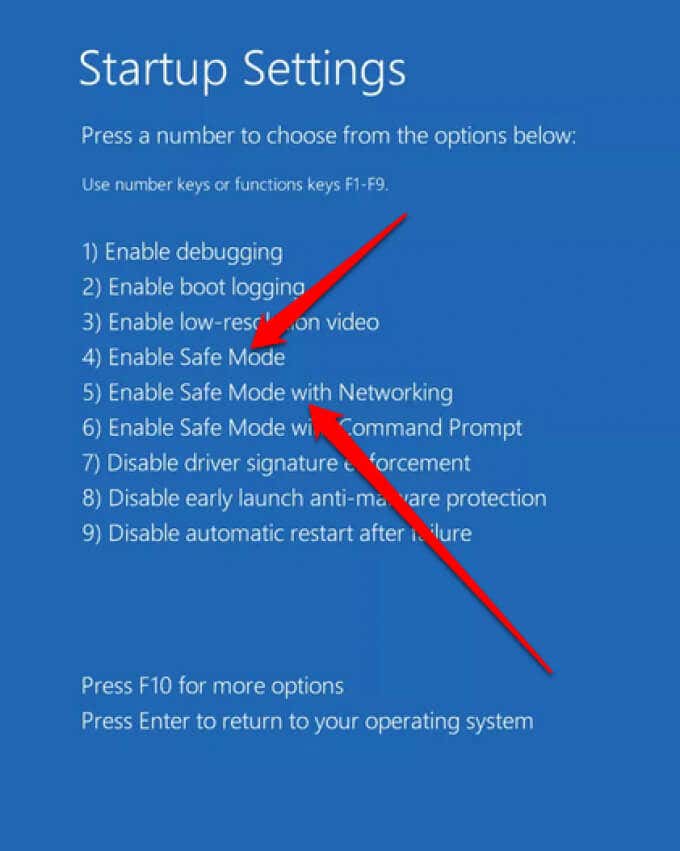
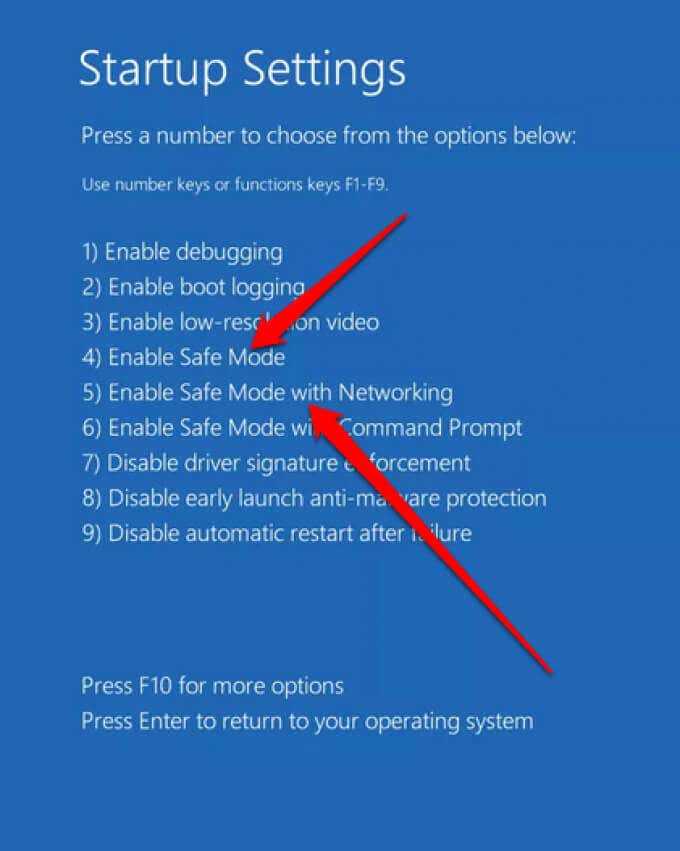
- Select Restart and once your PC restarts, select 4 to Enable Safe Mode or 5 for Safe Mode with Networking.
Note: If you’ve encrypted your computer, you may be asked to enter your BitLocker key before booting into Safe Mode. Safe Mode with Networking includes the services and network drivers needed to access other computers on your network and to access the internet.
Boot into Safe Mode from a Black or Blank Screen
There are several reasons why you may be seeing a blank or black desktop screen. For instance, you may have encountered the Windows 10 Black Screen of Death or there’s a problem with the screen.
You can still enter Windows Safe Mode from a black or blank screen, but you’ll need to enter the WinRE (Windows Recovery Environment) first.
- Press the power button and hold it down for 10 seconds until the device shuts down.
- Press the power button again to power the computer back on.
- When you see the manufacturer’s logo appear on your screen, hold down the power button again for 10 seconds to turn off the computer and then power it back on.
- Once Windows restarts, downpress the power button to turn off the computer, and then press the power button again to power it on.
- Allow the device to fully restart and you’ll enter the WinRE.
- Select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- Once your PC restarts, select Enable Safe Mode (4) or Safe Mode with Networking (5).
Boot into Safe Mode from Settings
If you can log into Windows 10, you can enter Safe Mode from the Settings app.
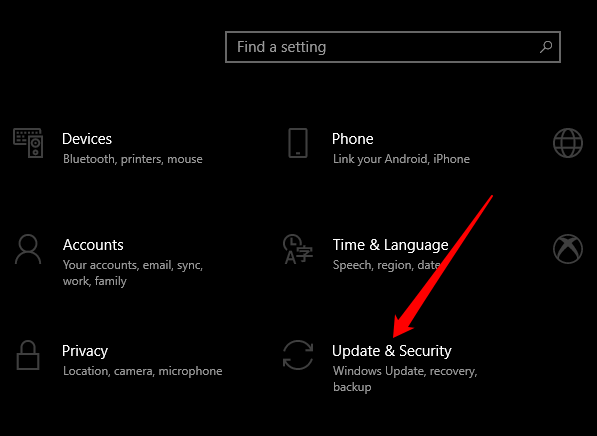
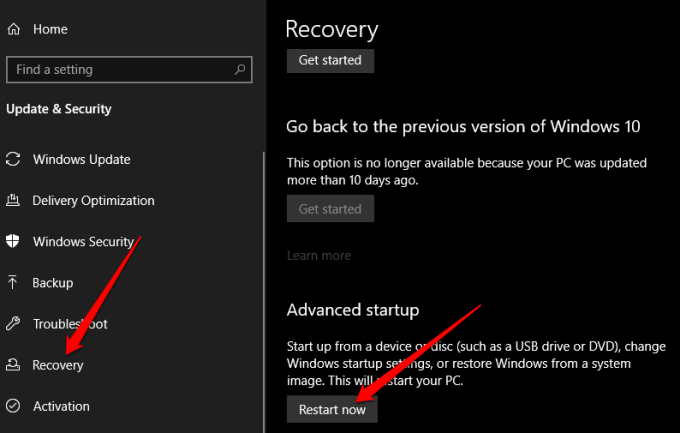
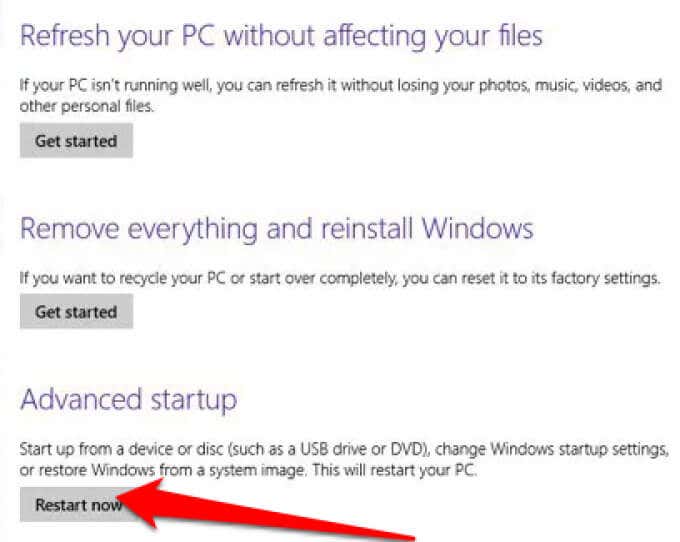
- Select Start > Settings > Update & Security.
- Next, select Recovery > Advanced startup > Restart now.
- Select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart on the Choose an option menu, and then select Enable Safe Mode or Safe Mode with Networking.
From a Recovery Drive
You can create a recovery drive if you don’t have one already and use it to access Safe Mode.
- Connect the recovery drive and power on your computer. Press Windows logo key + L to get to the sign-in screen and then use the steps to restart your computer in WinRE.
- In the Choose an option menu and select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart. Select Enable Safe Mode (4) or Safe Mode with Networking (5).
Note: If you don’t see the Choose an option menu, your computer may not be set up to boot from a drive, but you can change the boot order.
Using System Configuration
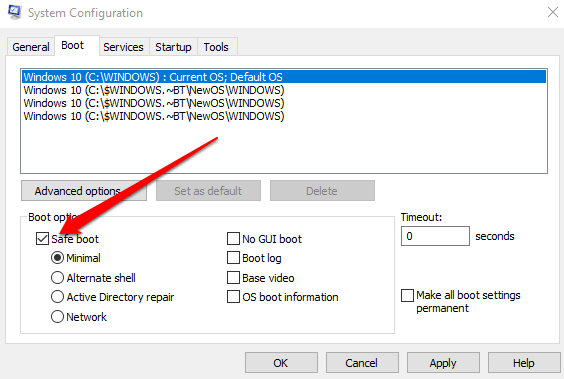
You can also use the System Configuration tool to enter into Windows Safe Mode.
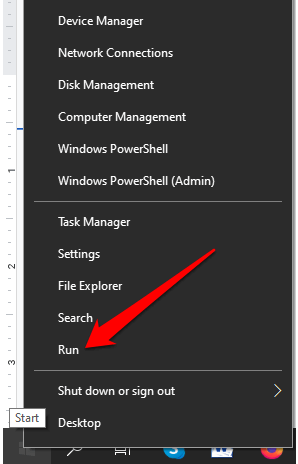
- Right-click Start > Run.
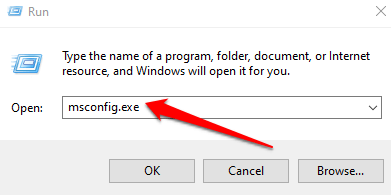
- Type msconfig.exe in the Run dialog box and press Enter.
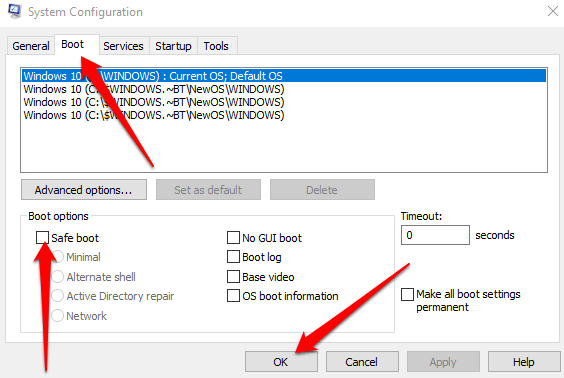
- Select the Boot tab in the System Configuration window, select Safe Boot under Boot options and press OK.
- If Windows prompts you to restart your computer, select Restart to access Safe Mode.
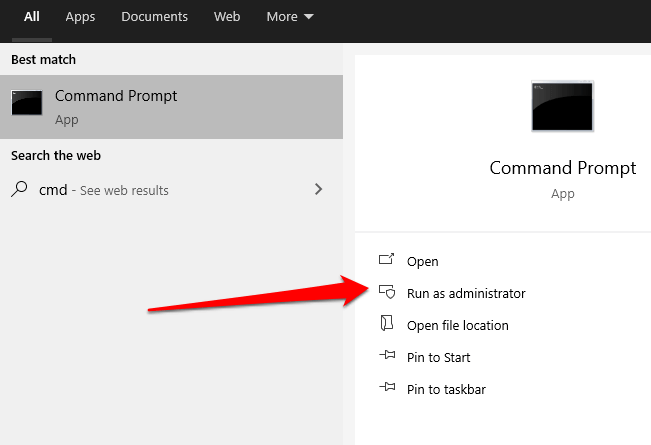
Using Shutdown Command in Command Prompt
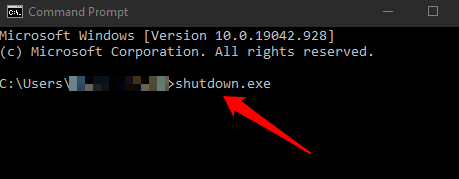
You can enter Safe Mode using the shutdown.exe command in Command Prompt.
- Type CMD in the search field and select Command Prompt > Run as administrator.
- Next, type shutdown.exe command and press Enter.
- Windows will restart in WinRE, sign you out and load the Choose an option screen. From here, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
- Select 4 or 5 depending on the Safe Mode option you want to boot into.
Exit Safe Mode in Windows 10
To exit Safe Mode in Windows 10, simply restart your device.
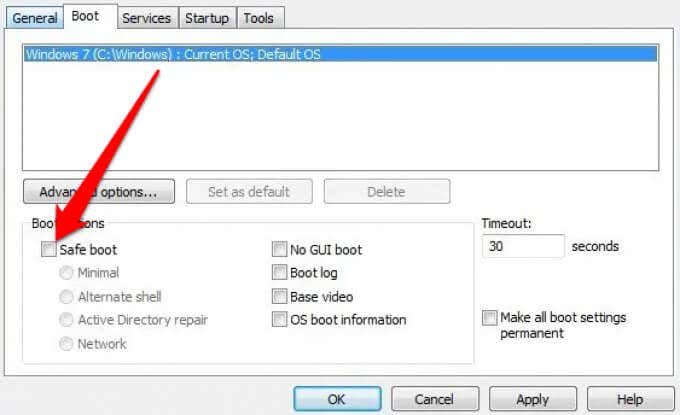
Alternatively, you can open the System Configuration tool again, select Boot tab and then deselect the Safe Boot checkbox under Boot options.
Windows 8 and 8.1
Like Windows 10, you can access Safe Mode in Windows 8 from the Startup Settings menu in Advanced Startup Options.
You can access the Advanced Startup Options by holding down the Shift key and selecting Restart. However, this method won’t work with the on-screen keyboard, so you’ll need to connect a physical keyboard to your computer to open the menus this way.
Alternatively, you can use the Settings menu to access the Advanced Startup Options menu and boot into Safe Mode in Windows 8/8.1.
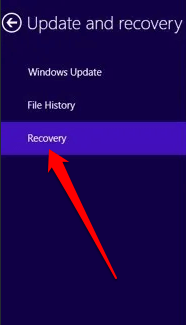
- Open the Charms bar and then select Change PC Settings.
- Select Update and Recovery > Recovery.
- Next, select Restart now from the Advanced startup section.
- In the Choose an option menu, select Troubleshoot > Advanced Startup Options > Startup Settings > Restart. Once your PC restarts, select a Safe Mode option by pressing 4 or 5 (or F4 or F5).
- Wait for Safe Mode to load and you’ll see the normal login screen when your computer starts.
- Login with your administrator credentials, make the necessary changes in Safe Mode and then restart your computer to exit Safe Mode.
Windows 7
Microsoft is no longer supporting Windows 7, which means you will no longer receive security updates and tech support. However, you can still enter Safe Mode in Windows 7 from the System Configuration utility.
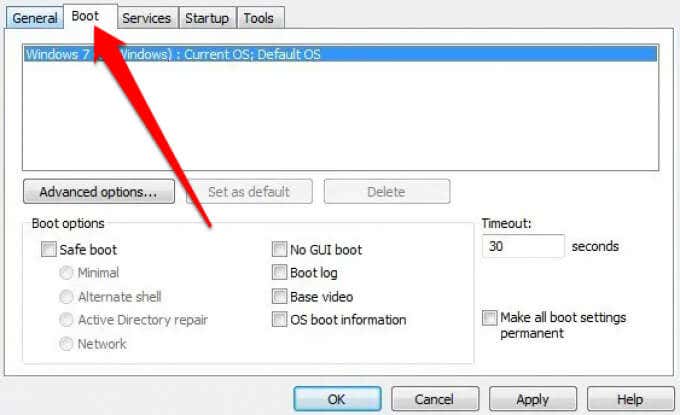
- Search for msconfig and then select the Boot tab in the System Configuration utility window.
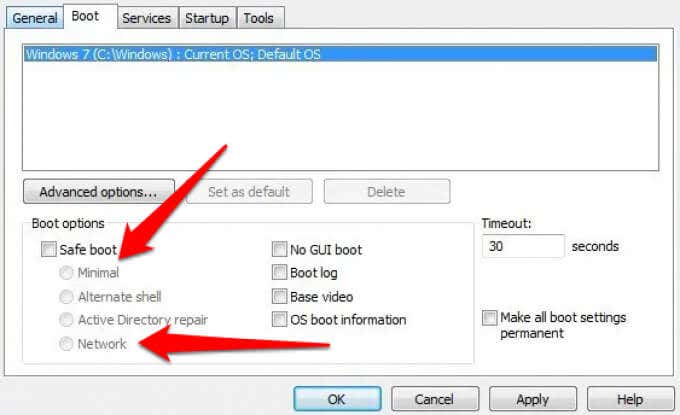
- Select the checkbox next to Safe Boot under the Boot Options section.
- Next, select Minimal to enter Safe Mode or Network to enter Safe Mode with Networking, and then select OK.
- Select Restart.
Windows XP
Microsoft also ended support for Windows XP. While you’ll no longer receive security updates or patches, you can still access Safe Mode in the operating system.
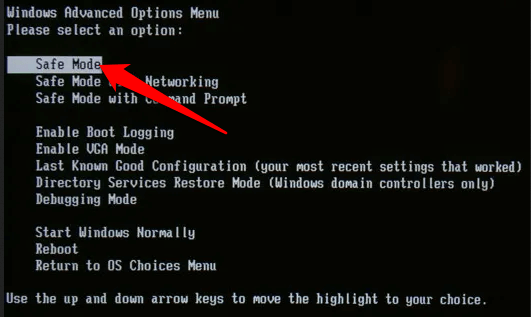
- Power on your computer if it’s off and press the F8 key repeatedly when the first screen appears.
- Select Safe Mode from the Advanced Options Menu and then press Enter.
- Select Administrator to enter your password when the Windows XP desktop appears.
If your computer was already powered on, use the steps below.
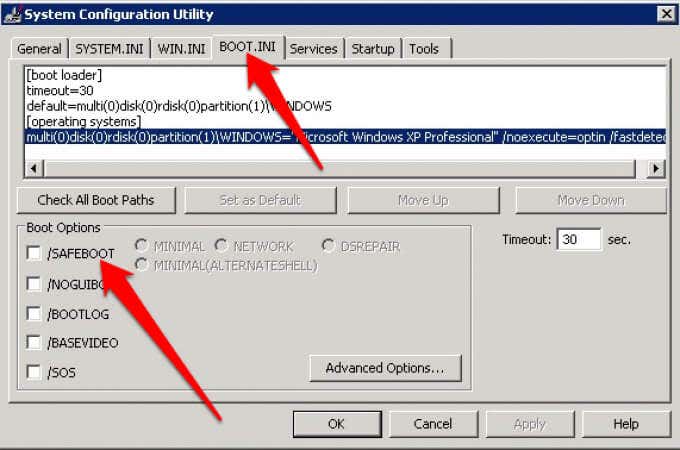
- Select Start > Run. Type msconfig in the Run dialog box and press Enter to open the MS Configuration Utility.
- Select Boot.INI tab and then select /SAFEBOOT under Boot Options.
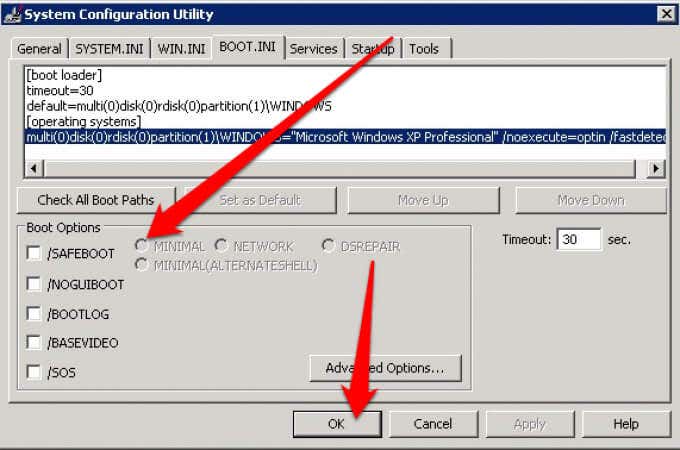
- Next, select Minimal > OK and then select Restart when prompted to.
- Once you’re done troubleshooting in Safe Mode, repeat the same steps but deselect the /SAFEBOOT option to prevent your computer from starting in Safe Mode.
Solve All Kinds of Problems in Safe Mode
Knowing how to access Safe Mode can help you troubleshoot and complete several functions including scanning for malware, uninstalling software, updating old drivers and restoring your entire system.
You may also be able to troubleshoot issues like Blue Screen of Death errors and other problems involving DLL files and device drivers.
Leave a comment and let us know whether this guide helped you access Windows Safe Mode on your computer.
Related Posts
- How to Reset Your Computer Password If You Lock Yourself Out
- Transfer Files from Windows XP, Vista, 7 or 8 to Windows 10 using Windows Easy Transfer
- How to Change the Clock To Military Time in Windows
- Best Ways to Quickly Hide Windows Applications
- Restart the Explorer.exe Process Correctly in Windows
Elsie is a technology writer and editor with a special focus on Windows, Android and iOS. She writes about software, electronics and other tech subjects, her ultimate goal being to help people out with useful solutions to their daily tech issues in a simple, straightforward and unbiased style. She has a BCom degree in Marketing and currently pursuing her Masters in Communications and New Media. Read Elsie’s Full Bio